能量估算公式:
\[Power = \alpha C V_{DD}^2 f\]
将造成每动作能量值差异的主要原因分为四类:
(1)动作特性
(2)数据特性
(3)时钟门控
(4)特定设计的优化
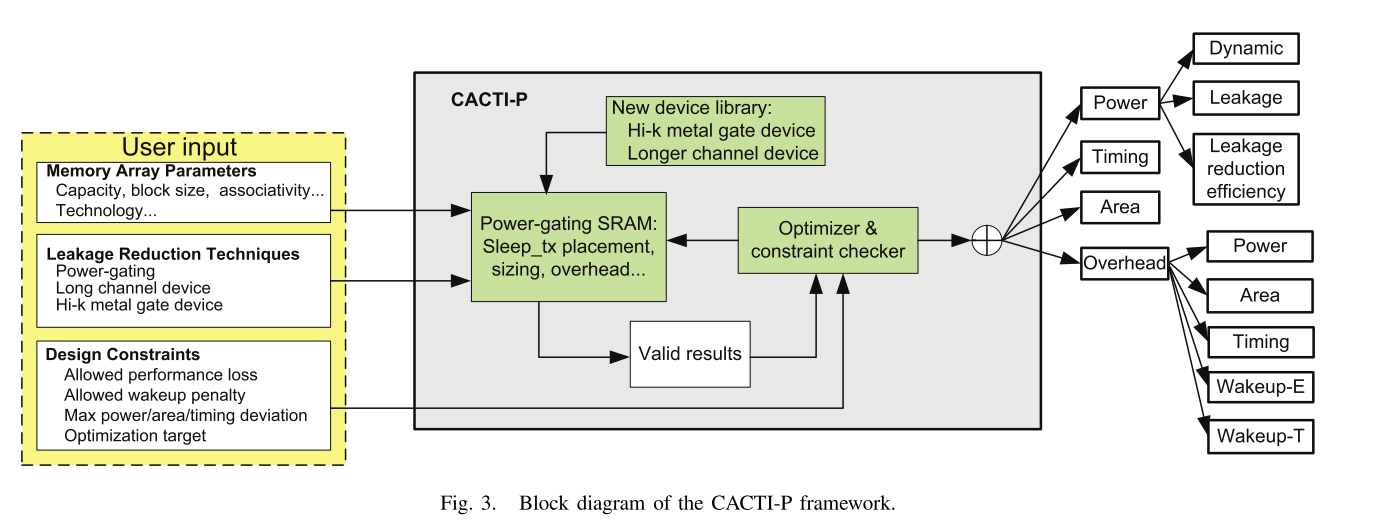
底层能量主要通过两个插件进行分析:CACTI和Aladdin。
CACTI
专门针对SRAM/DRAM/Chache的能量估算。
image-20230310155149259
Cacti是一种用于估计高速缓存和内存的访问时间、能耗和面积的工具。Cacti基于一个参数化的模型,可以根据不同的设计选择和技术节点来计算缓存或内存的性能和功耗。Cacti使用了一种分层结构来描述缓存或内存的组织,包括阵列、子阵列、行解码器、列解码器、位线驱动器、感应放大器等。Cacti还考虑了电路级别的因素,如线路电容、电阻、晶体管尺寸等。
Cacti能量评估器的原理是通过建立一个能量模型来计算每个组件在不同操作模式下(读取、写入或空闲)消耗的能量。能量模型包括静态功耗和动态功耗两部分。静态功耗主要由晶体管漏电流引起,与操作模式无关;动态功耗主要由开关活动引起,与操作模式有关。Cacti使用了一些简化的假设来估计开关活动率和电荷/放电电容值。最后,Cacti将每个组件的能量相加得到整个缓存或内存的总能量。
1 2 3 exec_list = [cacti_exec_path, '-infile' , cfg_file_name] subprocess.call(exec_list, stdout=temp_output)
DRAM
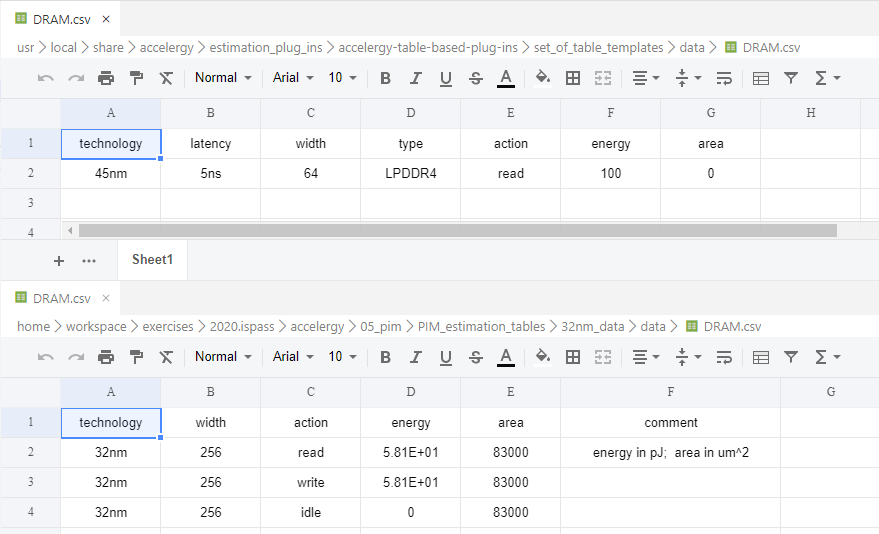
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 def DRAM_estimate_energy (self, interface ): action_name = interface['action_name' ] width = interface['attributes' ]['width' ] energy = 0 if 'read' in action_name or 'write' in action_name: tech = interface['attributes' ]['type' ] if tech == 'LPDDR4' : energy = 8 * width elif tech == 'LPDDR' : energy = 40 * width elif tech == 'DDR3' : energy = 70 * width elif tech == 'GDDR5' : energy = 14 * width elif tech == 'HBM2' : energy = 3.9 * width else : energy = 0 return energy def DRAM_estimate_area (self, interface ): return 0
SRAM
# Cacti only estimates energy for SRAM size larger than 64B
(512b)
# Cacti only supports technology that is between 22nm to 180 nm
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 if address_delta == 0 and data_delta == 0 : interpreted_entry_key = ('idle' , tech_node, size_in_bytes, wordsize_in_bytes, n_rw_ports, desired_n_banks) energy = self.records[interpreted_entry_key] else : idle_energy = self.records[('idle' , tech_node, size_in_bytes, wordsize_in_bytes,n_rw_ports, desired_n_banks)] address_decoding_energy = (self.records[desired_entry_key] - idle_energy) * 0.3 * address_delta/desired_n_banks memory_cell_access_energy = (self.records[desired_entry_key] - idle_energy) * 0.7 * data_delta energy = address_decoding_energy + memory_cell_access_energy + idle_energy return energy
Cache底层就是SRAM,两者CACTI输入参数对比如下:
image-20230322203356839
Aladdin
datapath(包括循环迭代并行性、流水线、数组分区和时钟频率,aladdin)+
memory(缓存层次结构,DRAMSim2)
image-20230310155559855
aladdin是一种用于估计加速器的性能、能耗和面积的工具。aladdin基于一个高层次的模型,可以根据不同的算法和架构来计算加速器的性能和功耗。aladdin使用了一种基于动态追踪(dynamic
trace)的方法来描述加速器的行为,包括内存访问、计算操作、控制流等。aladdin还考虑了电路级别的因素,如时钟频率、电压、晶体管尺寸等。
aladdin能量评估器的原理是通过建立一个能量模型来计算每个组件在不同操作模式下(读取、写入或空闲)消耗的能量。能量模型包括静态功耗和动态功耗两部分。静态功耗主要由晶体管漏电流引起,与操作模式无关;动态功耗主要由开关活动引起,与操作模式有关。aladdin使用了一些简化的假设来估计开关活动率和电荷/放电电容值。最后,aladdin将每个组件的能量相加得到整个加速器的总能量。
内部数据是40nm和45nm的器件的表格,通过缩放得到不同位宽/深度的能耗和面积。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 def oneD_quadratic_interpolation (desired_x, known ): """ utility function that performs 1D linear interpolation with a known energy value :param desired_x: integer value of the desired attribute/argument :param known: list of dictionary [{x: <value>, y: <energy>}] :return energy value with desired attribute/argument """ ordered_list = [] if known[1 ]['x' ] < known[0 ]['x' ]: ordered_list.append(known[1 ]) ordered_list.append(known[0 ]) else : ordered_list = known slope = (known[1 ]['y' ] - known[0 ]['y' ]) / (known[1 ]['x' ]**2 - known[0 ]['x' ]**2 ) desired_energy = slope * (desired_x**2 - ordered_list[0 ]['x' ]**2 ) + ordered_list[0 ]['y' ] return desired_energy
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 def intmultiplier_estimate_energy (self, interface ): this_dir, this_filename = os.path.split(__file__) nbit = interface['attributes' ]['datawidth' ] action_name = interface['action_name' ] if action_name == 'mult_gated' : interface['action_name' ] = 'idle' csv_nbit = 32 csv_file_path = os.path.join(this_dir, 'data/multiplier.csv' ) energy = AladdinTable.query_csv_using_latency(interface, csv_file_path) if not nbit == csv_nbit: energy = oneD_quadratic_interpolation(nbit, [{'x' : 0 , 'y' : 0 }, {'x' : csv_nbit, 'y' : energy}]) if action_name == 'mult_reused' : energy = 0.85 * energy return energy
环境配置
1、安装anaconda,python>=3.8
2、在accelergy文件夹下执行pip install .,自动地安装
3、发现accelergy被自动安装到了\home\june\.lacal\bin中,因此我们在\home\june\.bashrc文件中添加一句
1 export PATH="$PATH :/home/june/.local/bin"
然后再source .bashrc激活配置
4、然后acecerlgy就成了可执行的命令。
1 2 cd examples/hierarchy/inputaccelergy -o ../output/ *.yaml components/*.yaml -v 1
accelergy
使用 Timeloop 映射探索 ,Timeloop 使用 DNN
加速器的关键架构和实现属性的简洁统一表示来描述广泛的硬件架构空间。在精确能量估算器的帮助下,Timeloop
通过映射器为任何给定工作负载生成准确的处理速度和能效特征,该映射器找到在指定架构上安排操作和暂存数据的最佳方式。
使用Accelergy能量估算 ,Accelergy作为能量估算器,提供灵活的能量估算,以促进Timeloop的能量表征。Accelergy允许任意加速器架构设计规范,这些设计由用户定义的特定于设计的高级复合组件和用户定义的低级基元组件组成,这些组件可以通过第三方能量估算插件 进行表征,以反映设计的技术相关特征。
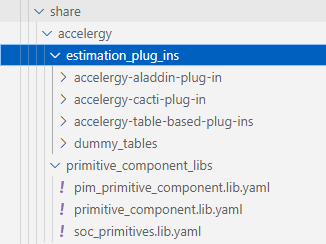
estimater
image-20230213161912908
estimation_plug_ins/accelergy-aladdin-plug-in/aladdin.estimator.yaml
estimation_plug_ins/accelergy-cacti-plug-in/cactimator.yaml
estimation_plug_ins/accelergy-table-based-plug-ins/table.estimator.yaml
architecture - eyeriss -
v0.2
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 1 smartbuffer_SRAM: eyeriss_like.weights_glb eyeriss_like.shared_glb 2 XY_NoC: eyeriss_like.weights_NoC eyeriss_like.ifmap_NoC eyeriss_like.psum_write_NoC eyeriss_like.psum_read_NoC 3 smartbuffer_RF: eyeriss_like.PE[0..167].weights_spad eyeriss_like.PE[0..167].ifmap_spad eyeriss_like.PE[0..167].psum_spad 4 intmac: eyeriss_like.PE[0..167].mac
ation没出现PE[139], PE[125], PE[111], PE[97],PE[83],PE[69], PE[55],
PE[41], PE[27], PE[13],也就是12*14的最后一列。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 version: 0.3 subtree: - name: eyeriss_like attributes: technology: 40nm local: - name: weights_glb class: smartbuffer_SRAM attributes: memory_width: 64 memory_depth: 1024 n_banks: 2 - name: shared_glb class: smartbuffer_SRAM attributes: memory_width: 64 n_banks: 25 bank_depth: 512 memory_depth: bank_depth * n_banks n_buffets: 2 update_fifo_depth: 2 - name: ifmap_NoC class: XY_NoC attributes: datawidth: 16 col_id_width: 5 - name: weights_NoC class: XY_NoC attributes: datawidth: 64 - name: psum_write_NoC class: XY_NoC attributes: datawidth: 64 - name: psum_read_NoC class: XY_NoC attributes: datawidth: 64 Y_X_wire_avg_length: 4mm subtree: - name: PE[0..167] attributes: memory_width: 16 local: - name: ifmap_spad class: smartbuffer_RF attributes: memory_depth: 12 buffet_manager_depth: 0 - name: weights_spad class: smartbuffer_SRAM attributes: memory_depth: 224 buffet_manager_depth: 0 - name: psum_spad class: smartbuffer_RF attributes: memory_depth: 24 buffet_manager_depth: 24 update_fifo_depth: 2 - name: mac class: intmac attributes: datawidth: 16
component - eyeriss - v0.3
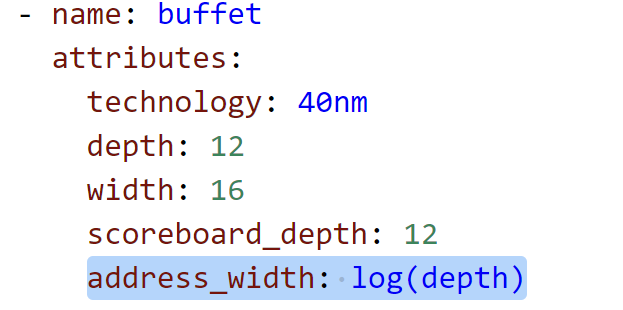
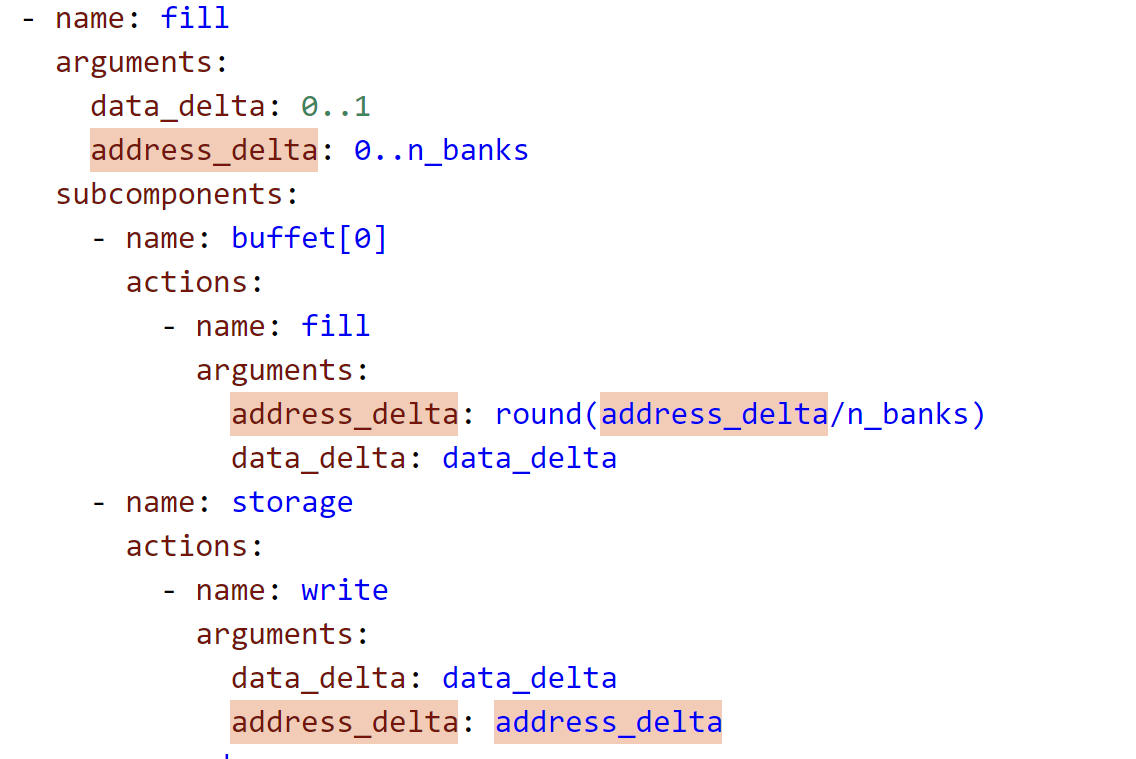
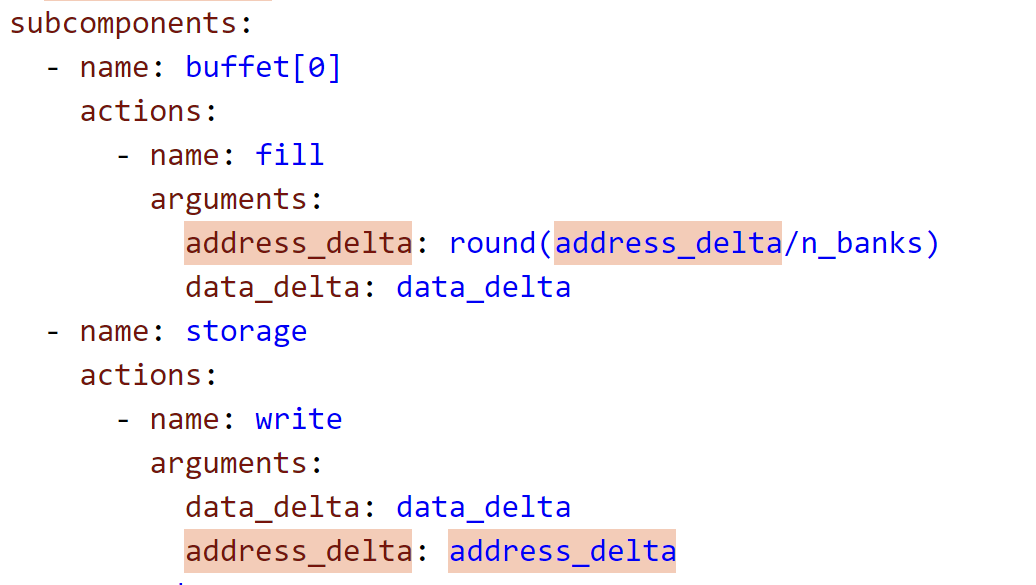
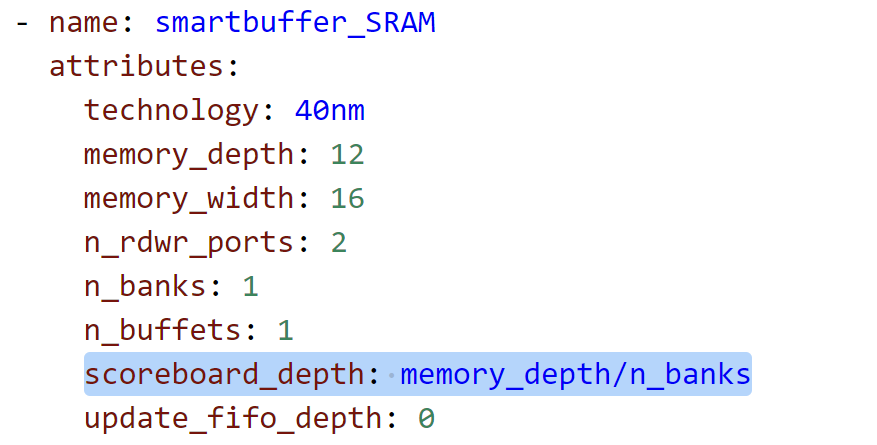
buffet:感觉是用来数据索引的 scoreboard(regfile)+data_FIFO*2+addr_FIFO*2
scoreboard_depth等于depth,
fill / read / update / idle
来自action_count的参数:address_delta,data_delta
buffet_collection_RF: buffet*n+ storage(regfile)
fill / read / update / idle
buffet_collection_SRAM: buffet*n+ storage(SRAM)
fill / read / update / idle
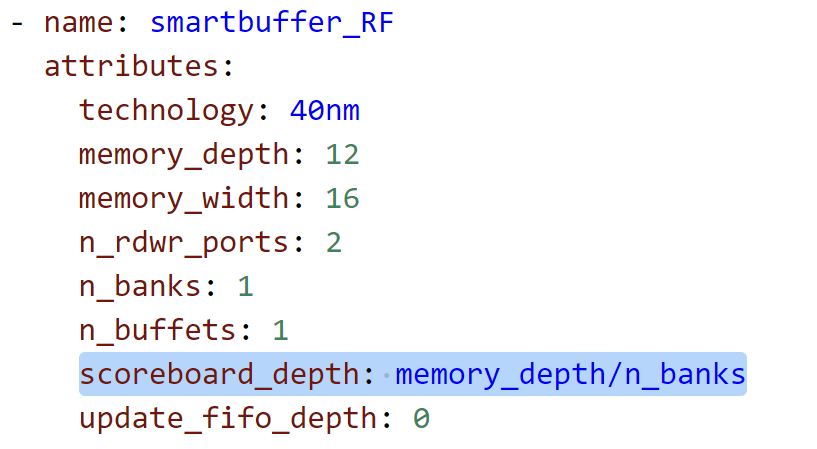
smartbuffer_RF
buffet_collection(buffet_collection_RF) +
address_generators(counter)*2
fill / read / update / idle
smartbuffer_SRAM
buffet_collection(buffet_collection_SRAM) +
address_generators(counter)*2
fill / read / update / idle
XY_NoC
Y_memory_controller[0..n_PE_rows-1](comparator) +
X_memory_controller[0..total_PEs-1](comparator) + Y_X_wire(wire)
transfer_random / transfer_repeated / idle
action count
问题记录:
1、action里的参数address_delta,data_delta是什么?(发现在PE里address_delta只出现0,1两种取值,data_delta全程只出现0,1两种取值)
2、NoC的action里的参数n_cols_per_row,n_rows是什么?
3、为什么weights_spad是smartbuffer_SRAM,而其他的是smartbuffer_RF?
4、3个spad里(ifmap,weights,psum)的buffet_manager_depth为啥设成0、0、24?memory_depth设成12,224,24?
5、
这4种运算代表啥?mac_gated应该就是zerogating的情况,idle是不工作,random是最耗电的,reused是重复上一次计算结果。
PIM
输入文件分析
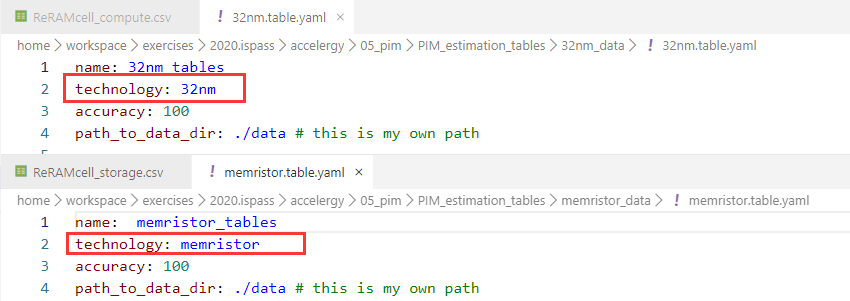
基于内存(忆阻器)的一个体系结构,输入文件中没有action_counts.yaml,输入的是PIM_estimation_tables文件夹。
1 accelergyTables -r ./05_pim/PIM_estimation_tables
image-20230213162512868
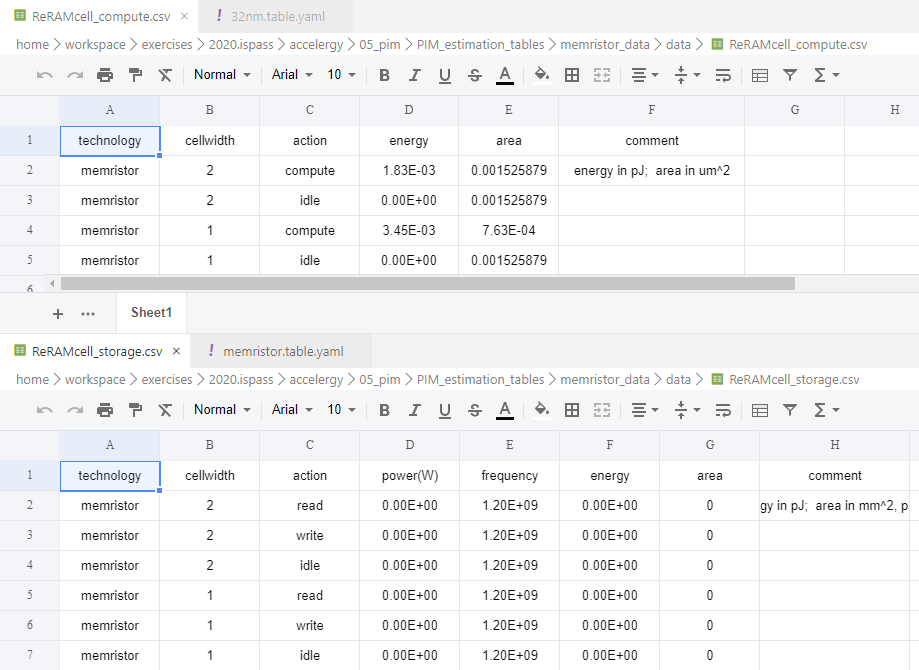
其中32nm文件夹存放传统的组件,有一部分已在安装的插件代码中出现过(比如DRAM.csv),有一部分是新定义的组件(如ADV.csv)。
memristor文件夹存放基于忆阻器的组件。
输出文件分析
没有energy_estimation.yaml,该文件用于评估原始组件的能量。其他输出文件都是有的。